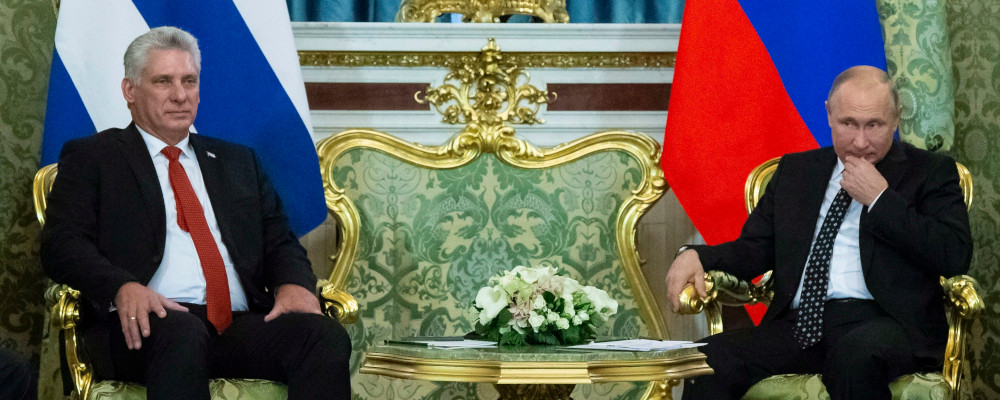
Alliances between authoritarian regimes are one of the greatest global threats facing democracy today. Collaboration between autocrats makes them stronger, and more effective at surveilling, isolating, and persecuting human rights defenders. Two such alliances are between Cuba and China, and Cuba and Russia. And the effects of these alliances on the pro-democratic Cuban movement are stark.
China dominates the telecommunications sector in Cuba, including the expansion of internet access on the island that has been done with Chinese technology and advice. This is concerning for the future of internet freedom in Cuba. China’s Great Firewall has managed to erase critical historical events, including the Tiananmen Square massacre, from the memory of new generations. China has 900 million internet usersDigital Authoritarianism and Nonviolent Action: Challenging the Digital Counterrevolution https://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep34109#metadata_info_tab_contents and only between 3 to 15 percent manage to circumvent the Great Firewall through use of virtual private networks (VPNs).Digital Authoritarianism and Nonviolent Action: Challenging the Digital Counterrevolution https://www.jstor.org/stable/resrep34109#metadata_info_tab_contents
The Cuban regime similarly censors internet access, and it likely sees the most repressive aspects of the Chinese system of internet control as a model worth emulating. Through the use of Chinese technology, censorship of websites, social media, application of internet outages, and blocking of VPN access, the Cuban regime is significantly reducing free spaces in Cuba for civil society to coordinate actions and organize mobilization for democratic change.
For its part, the Cuban regime supports China at international fora, including by actively supporting Beijing’s claims on Taiwan. The Cuban Foreign Ministry as well as its press agencies on the island and abroad actively defend and promote the so-called “one China” principle that establishes that the entire Asian giant, including the democratic island-nation of Taiwan, is one country with a government that has its capital in Beijing. They also actively condemn the U.S.’s position with respect to Taiwan. China may be motivated, at least in part, to use Cuba’s diplomatic influence in the region to influence the four Caribbean nations that still recognize Taiwan to switch to non-recognition.
On October 21, 2021, the Cuban regime delivered a statement62-nation joint statement supports China’s human rights promotion and protection https://newsus.cgtn.com/news/2021-10-22/62-countries-support-for-China-s-promotion-protection-of-human-rights-14yp7X3NRf2/index.html in the United Nations General Assembly on behalf of 62 countries praising China’s human rights record in Hong Kong, Xinjiang, and Tibet, despite vast evidence of gross human rights violations and atrocity crimes, including genocide, perpetrated by the Chinese Communist Party. In this way, this alliance between Cuba and China reveals the global implications of mutual complicity and how this contributes to forging a global culture of impunity for atrocity crimes.
Cuba is also allied with Russia. Just as the Cuban media repeats Chinese propaganda points on Taiwan, Hong Kong, Xinjiang, and Tibet, the Cuban media also reproduces disinformation disseminated by the Kremlin to justify its invasion of Ukraine. For example, Cuban state media refuses to recognize that there was even an invasion of Ukraine; it is instead described as “a special operation.” They also parrot Russian propaganda narratives about the need for Russia to “denazify” Ukraine, and blame criticisms of Vladimir Putin on “Russophobia,” ignoring the Russian regime’s responsibility for the brutal attacks against civilian populations.
This disinformation is broadcasted internationally by the Cuban regime through the Cubavision International signal via five satellites to more than 60 million people in America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. Despite Canada’s condemnation of the dissemination of disinformation about the war in Ukraine, the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) continues to authorize Cubavision International to be distributed in Canada.Revised list of non-Canadian programming services and stations authorized for distribution https://crtc.gc.ca/eng/publications/satlist.htm
Canada has been vocal against authoritarianism in Russia and, to a lesser extent, China. However, Canada has been relatively silent against authoritarianism in Cuba. This does not represent a principled human rights policy.
Besides Cuba’s key authoritarian alliances with Russia and China, the Cuban regime has a disastrous record of human rights abuses. Cuba is one of the oldest dictatorships in the world, and the regime has increasingly cracked down on human rights defenders. Following the July 2021 pro-democratic protests, the Cuban regime jailed so many political prisoners that it now has more arbitrarily detained than Venezuela and Nicaragua combined.
The alliances between Cuba, China, and Russia are a threat to democracy. They facilitate digital authoritarianism, the global expansion of authoritarian norms, disinformation, and impunity for atrocity crimes and human rights abuses. It is time for Canada to rethink its foreign policy towards Cuba, in the spirit of standing up against human rights violations—wherever they occur.
Recommended for You

David Polansky: As President Biden leaves the race, will the Democratic Party hodgepodge hold?

David Mulroney: Foreign Minister Joly, Xi Jinping’s China doesn’t do ‘dialogue’

J.L. Granatstein: Trudeau’s submarine charade

Amal Attar-Guzman: Canada’s global leadership is waning. Why not expand our influence closer to home?